Solutions
Technologies
Implementing Transcoding TV signals streams greatly enhanced our guest experience. Seamless compatibility and high-quality streams allow guests to enjoy a wide range of channels effortlessly. Exceptional technical support ensured a smooth integration. Strongly recommended.
Felix Müller
Chief Engineer
Transcoding TV signal streams has revolutionized operations at Lakeside Hotel. It greatly improves guest access to a diverse range of TV content. Flexible setup options and outstanding technical support provide a hassle-free experience. Guests are very pleased.
Emma de Vries
Technical Manager
Downloads
Transcoding TV Signal Streams
This technical documentation section outlines the process, technologies involved, and considerations for transcoding TV signal streams.
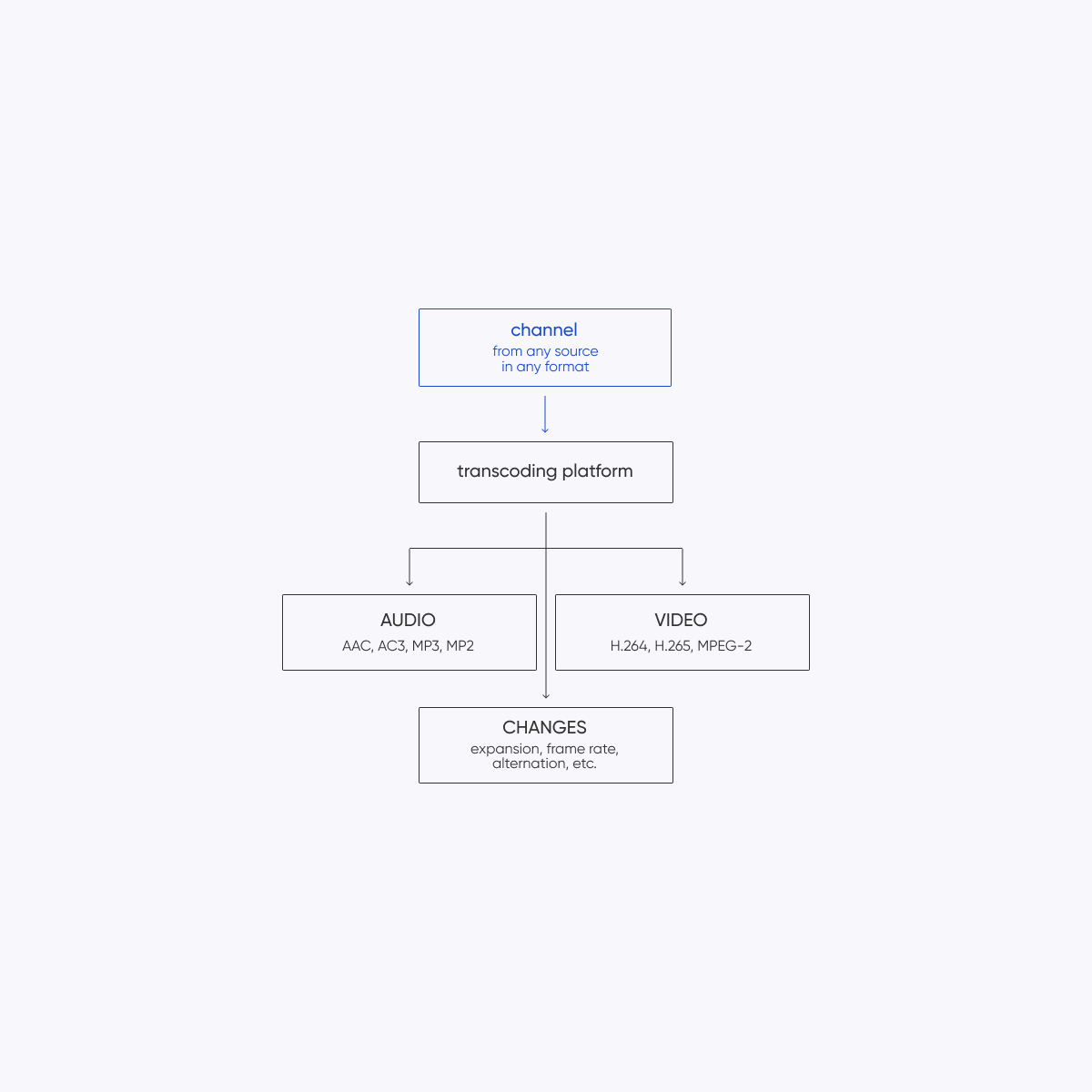
Key Components
- Source TV Signals: The original television signals received from cable, satellite, or terrestrial broadcasters.
- Transcoding Server: The hardware or software responsible for performing the transcoding process, converting the source TV signals from one format to another.
- Codec Libraries: Software components or algorithms used for encoding and decoding audio and video data during the transcoding process.
- Network Infrastructure: The network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and bandwidth capacity, necessary for transmitting the transcoded TV signal streams.
- Playback Devices: Devices such as TVs, computers, tablets, and smartphones used by viewers to access and playback the transcoded TV signal streams.
Transcoding Process
- Signal Analysis: The source TV signals are analyzed to determine their encoding format, resolution, bitrate, and other parameters.
- Codec Selection: Based on the analysis, appropriate codecs are selected for transcoding the TV signal streams. Common video codecs include H.264, H.265 (HEVC), and VP9, while audio codecs may include AAC, MP3, or Dolby Digital.
- Transcoding: The selected codecs are applied to the source TV signals to convert them into the desired encoding format. This process may involve compression, decompression, and format conversion.
- Quality Optimization: Transcoding settings are adjusted to optimize the quality of the transcoded TV signal streams while minimizing bandwidth usage and maintaining compatibility with playback devices.
- Network Transmission: The transcoded TV signal streams are transmitted over the network infrastructure to the playback devices using appropriate streaming protocols such as RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol) or HLS (HTTP Live Streaming).
Technologies and Protocols
- Video Codecs: Standards such as H.264, H.265 (HEVC), VP9, and AV1 are commonly used for video transcoding.
- Audio Codecs: Common audio codecs include AAC (Advanced Audio Coding), MP3, and Dolby Digital.
- Streaming Protocols: Protocols like RTSP, HLS, MPEG-DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP), and Smooth Streaming are used for transmitting transcoded TV signal streams over the network.
- DRM (Digital Rights Management): Technologies used to protect copyrighted content during transcoding and transmission.
How to Start
Assess your hotel's infrastructure and requirements
Determine whether you already have a cable infrastructure in place or if you need to set up a new system. Consider factors such as the number of rooms, the desired channel lineup, and any additional features like video-on-demand or interactive services. This assessment will help you determine the scope of the project and the necessary equipment and resources.
Learn MoreChoose a reliable TV signal provider and system
Consult with the provider to discuss your specific requirements and ensure that their system can meet your needs. Consider factors like the number and variety of channels available, the user interface for guests, content management features, and technical support.
Learn More